.jpg)
CONTENTS
1. Geography and population of Slovenia
2. Official language of Slovenia
3. Currency in Slovenia
4. Internet in Slovenia
5. Economic development in Slovenia
6. Job in Slovenia
7. Working days and holidays in Slovenia
8. Slovenian mentality
9. Advertising in Slovenia
10. Cryptocurrency in Slovenia
1. Geography and population of Slovenia
Population of the country – 2.1 million people. 83% of Slovenes live here. There are also Serbs, Croats, Bosnians, Albanians, Hungarians, Macedonians, Italians and Montenegrins.
Slovenia is a small state in Central Europe with beautiful nature, history and dynamic economy. The country is part of the European Union and the Schengen Agreement. Slovenia is located at the junction of the Balkans and Central Europe, in the eastern part of the Alps and the northern Adriatic. The country borders in the north with Austria, in the west with Italy, in the southeast with Croatia, in the northeast with Hungary.
General information about Slovenia:
Capital: Ljubljana
Area: 20,000 km2
Calling code: +386
Internet top level domain: .si
Population: 2,100,000

Timezone:
Central European Summer Time (CEST) – UTC +02:00
Standard time (Central European Time (CET), UTC +01:00) starts with October 31, 2021
Slovenia’s population:
- Slovenia had a population of 2.08 million in January 2021.
- Slovenia’s population increased by 34 (+ 0.002%) between January 2020 and January 2021.
- 50.2% of Slovenia’s population is female, while 49.8% is male (note: the United Nations does not publish data for other genders than ‘female’ and ‘male’).
- 55.3% of Slovenia’s population lives in urban centers, while 44.7% lives in rural areas.
2. Official language of Slovenia
The official and spoken language of Slovenia is the Slovenian language. It is spoken by 91.1% of the population (according to the 2002 census). Also, a large part of the population speaks English, Hungarian and Italian.
According to Article 11 of the Constitution of Slovenia, the Slovenian language is the only official. Television, radio, newspapers, commercials, instructions for use and other media can only be in Slovenian, foreign languages are allowed only with subtitles or translation. After Slovenia joined the European Union on May 1, 2004, Slovenian became one of its official languages.
In many cities in Slovenia, signs in any other language than Slovenian are prohibited.
3. Currency in Slovenia
On May 1, 2004, the Republic of Slovenia joined the European Union. For two and a half years, preparations were underway for the transition to the euro. On January 1, 2007, Slovenia abandoned its national currency, the tolar, after entered the eurozone and introduced the euro as an official currency. Thus, the currency of Slovenia today is the euro, consisting of 100 euro cents. Tolar was called the monetary unit of Slovenia in 1991-2006.
Slovenia’s currency is the euro. Credit cards are accepted in many shops and restaurants.
A hotel room for two can be rented for 30-40 euros (prices vary greatly depending on the season, the star rating of the hotel and location). Dinner or lunch in a restaurant and cafe will cost 20-30 euros. A pint of beer costs 2-4 euros. Gratuities are usually included in the bill. If not, then it is customary to leave 10-15% of the invoice amount.
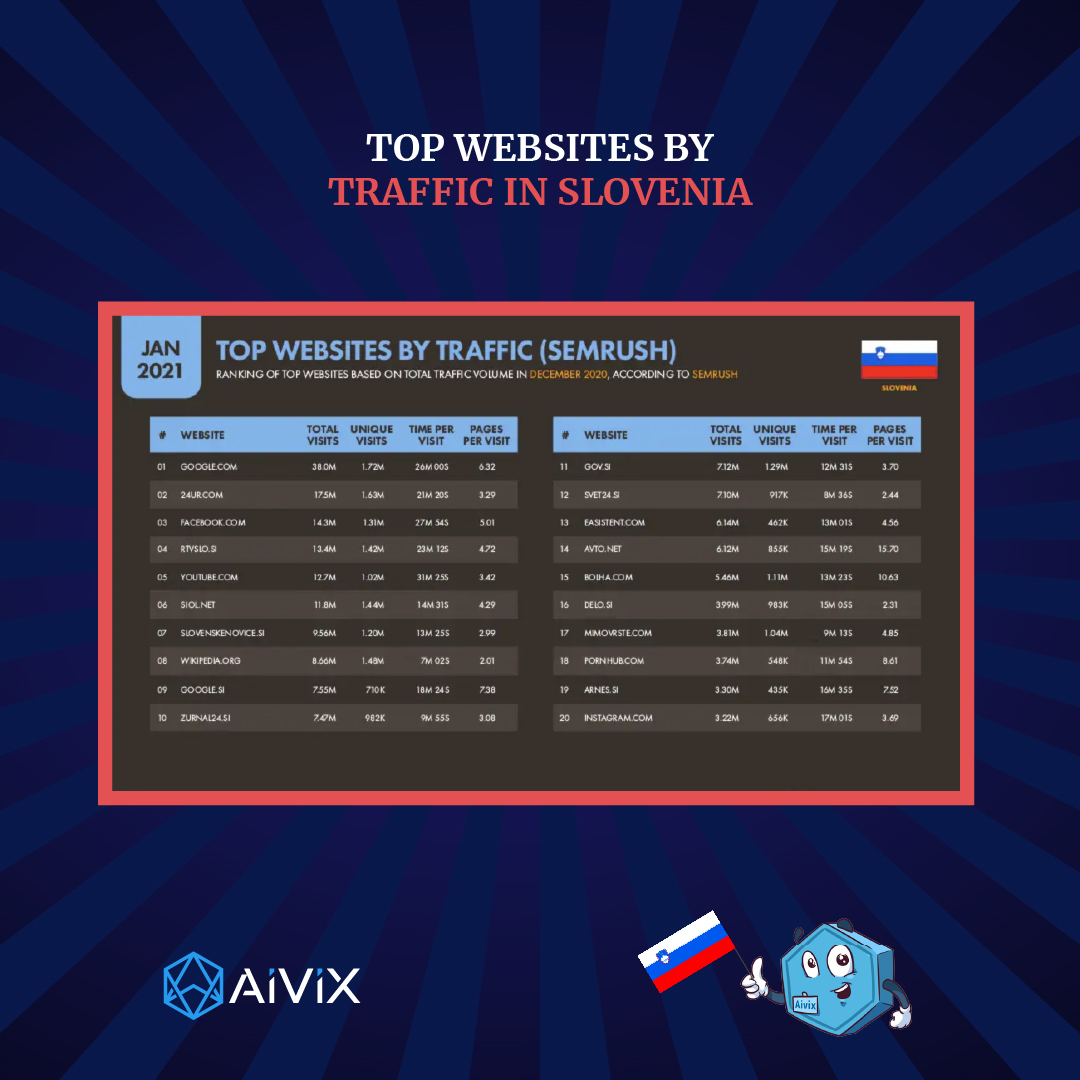
4. Internet in Slovenia
Internet users in Slovenia
- There were 1.75 million internet users in Slovenia in January 2021.
- The number of internet users in Slovenia increased by 62 thousand (+ 3.7%) between 2020 and 2021.
- Internet use in Slovenia raised to 84.0% in January 2021.
Internet censorship and surveillance
There are no government restrictions on internet access or credible reports of government monitoring emails or chats without proper legal authority. The constitution and law provide for freedom of speech and press, and the government generally respects these rights. However, the law prohibits hate speech, including incitement to intolerance, as well as violence. The law criminalizes defamation that harms a person’s honor or name. The constitution and laws prohibit arbitrary interference with privacy, family, home, or correspondence, and the government generally enforces these prohibitions in practice. Individuals and groups are free to participate in expressing opinions over the Internet.
The independent organization Helpline Spletno Oko (Web Eye) monitors hate speech and child pornography on the Internet and received an average of 62 reports and tips per month in 2012.
On January 28, 2010, the Slovenian National Assembly adopted amendments to the law regulating gambling. According to the law, Internet service providers are responsible for blocking access to gambling sites that are not licensed by the Slovenian government.

5. Economic development in Slovenia
Slovenia and the Economy: Very Fast Recovery and Strong Economic Growth Expected
The Slovenian economy is expected to recover very quickly. This is very good news for all foreign entrepreneurs who intend to expand their business in the EU. According to the latest data from the Bank of Slovenia, this year the country’s economy will grow by 5.2%. The news is unambiguously positive – moreover, it is predicted that Slovenia will reach the pre-crisis level of GDP, most likely, already next year! Slovenia and the economy is having now the best time to start a business in Slovenia due to good forecasts for the next years!
Slovenia and Economy – Forecast in Figures
This year, economic growth is projected at 5.2%. It is expected to remain high next year as well – forecasted at 4.8%. Growth is expected to be driven by both domestic and foreign demand. Inflation, despite strengthening, should remain below the medium-term target – i.e. below or close to 2%.
Slovenia and the economy: What about the upcoming years?
Forecasts for 2022 and 2023 also promise economic growth. Thus, in 2022, the economy is expected to grow by 4.8%, and in 2023 – by 3.1%. Exports are expected to grow by 11.1% this year and imports by 11.6%. Employment is expected to grow from year to year, this year from 0.7%, and in subsequent years will grow by about 1.5% annually.
You have to pay for a high income – income tax is calculated on the basis of the salary and can go up to 50%. The minimum rate is 16%. In addition, the state will have to give interest in the following cases:
– upon purchase (2%);
– VAT (2%);
– when registering purchased property or goods (0.01-0.5%);
– in case of capital gain (25%);
– upon receipt of an inheritance (0-39%);
– in case of profit by legal entities – corporate tax (17%);
– upon donation (0-3%).
If the annual income of an individual is less than 8 thousand euros, then income tax is calculated at the minimum rate. The maximum rate is paid on income exceeding 70.9 thousand euros.
6. Job in Slovenia
According to official figures from the Slovenian Statistical Office, the average salary in Slovenia in 2021 is 1,856.20 euros per month. After all mandatory deductions, local workers have €1,253.71 at their disposal. The highest revenues are provided by the supply of electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning – 2,906 euros. In the public sector of the Slovenian economy, they earn 2,096.96 euros per month (1,351.52 euros net), and in the private sector 1,673.40 euros.
In conclusion, we note that the unemployment rate in Slovenia is about 9-10%, and the income tax rate in 2021 varies from 16% (income up to 8,500 euros per year) to 50% (income over 72,000 euros per year)
Salaries by profession in Slovenia:
Medical staff – €1800
Lawyer – €2000
Marketing specialist – €2250
Business Analyst – €2750
Education field – €1200
Pension system
Income in declining years depends on the hard work of local residents, because the pension is calculated on the basis of a salary. On average, it is 62-69% of the average salary level, which is equal to 700-800 euros. Women are escorted to a well-deserved rest at the age of 61, and men – 2 years later. By the way, in terms of pensions, Slovenia closes the gold “four” behind Portugal, the Czech Republic and Finland.
Average salary by region in Slovenia:
– In the Central Statistical Region, salaries in Slovenia amounted to 2,249.67 euros and increased by 2.1% in March.
– In the Pomurje region, it grew the most – by 6.7%.
– The lowest salary in Slovenia is in the Primorsko-Notranj region, where it is 1,740.94 euros.
7. Working days and holidays in Slovenia
The working day in Slovenia starts at 7-8 am and ends at 15-16 pm. “Friday Party” is here on Thursday. Since on Friday, after work, Slovenes try to leave for nature, in another city, or else out of the country for the weekend.
Slovenia weekend public holidays:
January 1st-2nd – New Year’s Holidays. State national holiday since 1955. January 2nd was a day off until 2012 and then again from 2017 (Novo leto).
8 February is Preshern Day. State national holiday of Slovenian culture since 1946. (Prešernov dan).
April 27 is the day of resistance against the invaders. On this day in 1941 in Ljubljana it was decided to create a resistance organization (Dan upora proti okupatorju).
May 1st, May 2nd – National Labor Day has been celebrated since 1946 (Praznik dela).
June 25 – Statehood Day – a national public holiday in Slovenia. It is dedicated to June 25, 1991, when Slovenia officially became independent (Dan državnosti).
November 1 – Memorial Day or Day of the Dead is a national holiday in Slovenia, which is celebrated on November 1 in memory of the dead (Dan spomina na mrtve)
December 26 is the State Day of Independence and Unity (Dan samostojnosti in enotnosti).
8. Slovenian mentality
Slovenian culture boasts a wide variety of traditions, customs and rituals. Here the sweetness of the vine from the Croatian slopes, the Italian sun, German punctuality and the mountain songs of Austria are mixed.
Characteristics of the character of local residents
In most cases, they are very independent, serious and hardworking. When communicating, they are more restrained than temperamental Italian neighbors.
The restraint of Slovenes is manifested at every step – it is accepted to greet with a handshake; and public hugs and kisses are not at all accepted here. This should be done at home, not in public. The way to the heart of a local lies through flowers – the Slovenes love them very much.
You will hardly see fences around private estates, but elegant multi-colored flower beds, neat personal gardens and orchards are an obligatory attribute.
Culture of Slovenia
A calm, unhurried and measured lifestyle helps them to be in time everywhere. By the way, about academic performance – Slovenes do not like being late and are very punctual (no matter an informal meeting or an official event) – they arrive exactly at the appointed time. Even, it’s better to come to visit without a gift than to be late.
In the evening, the streets of Slovenia are always empty, as they spend evenings only with their families and go to bed very early.
But, for tourists it is important to know that they are too democratic towards people with a gay orientation. What may seem unacceptable to you is quite normal for Slovenes. Do not focus on what you see and do not show your dissatisfaction, these are the features of Slovenia.
It is not customary to talk about business and finance while eating. This rule applies even during dinner with a business partner. While eating, you need to relax and enjoy. You can talk about work only if the partner himself spoke about it.
Kisses and hugs are not as common here as among other Slavic peoples, only relatives and close friends kiss each other. Eye contact is very important. Slovenes adapt to the companion; therefore, you should behave yourself. The local will rather avoid answering than say something that, in his opinion, may offend somebody.
How to communicate with Slovenes
When meeting with them, you need to shake hands – both a man and a woman. It is better to talk calmly and quietly, they do not like boasters at all, they respect modesty and they try to be the same.
9. Advertising in Slovenia
Advertising on the Internet in Slovenia
Internet advertising in Slovenia based on static data increased in 2013. The Statistical Office of Slovenia published information stating that the number of companies that conduct their sales and advertising via the Internet increased in 2013.
More and more companies are making decisions about the sales and advertising of their companies over the Internet. The Statistical Office of Slovenia published information stating that the number of companies that conduct their sales and advertising via the Internet increased in 2013.
In 2013, 14% of companies already organized sales and took orders for products or services via the Internet. In 2012, there were only 11% of such companies. Almost all companies selling on the Internet received 95% of orders from Slovenian buyers. 42% of companies also worked with other EU countries and 20% of orders came from other non-EU countries.
1/5 of companies promote their services over the Internet.
The Internet is an important communication, marketing and advertising medium. Allowing you to interact with the end customer and partners at the same time. 84% of companies with 10 or more employees have their own website on the Internet.
If you decide to open an online store or promote your services over the Internet, contact our specialists and they will create a website for your company.
In social networks such as Facebook, Google+, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, Pinterest, 37% of companies have made their profile. 22% of companies pay for online advertising: for example, advertising on search engines or social media.
If you agree with the conclusion that the Internet and social networks are an important tool for promoting the company and your services, contact us and our specialists will support you in advertising your company on the Internet and in social networks.
Social media statistics for Slovenia
– In January 2021, there were 1.45 million social media users in Slovenia.
– The number of social media users in Slovenia increased by 120 thousand (+ 9.1%) between 2020 and 2021.
– In January 2021, the number of social media users in Slovenia was 69.8% of the total population.
Mobile connections in Slovenia
– There were 2.11 million mobile connections in Slovenia in January 2021.
– The number of mobile connections in Slovenia decreased by 41 thousand (-1.9%) between January 2020 and January 2021.
– The number of mobile connections in Slovenia in January 2021 was equivalent to 101.6% of the total population.



10. Cryptocurrency in Slovenia
Along with Estonia, Lithuania, Finland and the Czech Republic, Slovenia is one of the European countries to consider when planning a cryptocurrency business. The Slovenian government seeks to cement the country as one of the leaders among the EU member states in the field of blockchain technology. This is achieved through the usual tools: openness to new technologies, the application of tax incentives and increased transparency of operations in the field of digital assets.
Cryptocurrency status in Slovenia
Slovenian legislation currently defines cryptocurrencies as virtual currencies. This means that they cannot be either financial instruments or monetary funds in accordance with Slovenian legislation on payment services and systems.
In order to comply with international requirements for tax transparency, Slovenia has expanded the scope of the legislation on combating money laundering in operations with cryptocurrencies. Currently, any crypto exchange or broker is recognized by financial institutions for the purposes of AML legislation. Thus, such institutions must comply with the transparency and KYC procedures that apply to financial institutions.
Taxation of cryptocurrencies in Slovenia for individuals
The Finance Service of Slovenia (FURS) in 2017 in its guide first mentioned cryptocurrencies in relation to the taxation of capital gains from virtual currencies. Individual income in the form of bitcoins or other virtual currencies is subject to taxation. The taxable base is calculated based on the exchange rate of the cryptocurrency against the euro at the date of receipt of this cryptocurrency. A similar principle applies in the case of mining.
However, FURS notes that an individual’s income from trading bitcoins or other virtual currencies, as well as income from cryptocurrency rate fluctuations, is not taxable. This is due to the fact that, in accordance with the Slovenian Income Tax Law, capital gains are generally not applied on income from movable property or from financial derivatives. As mentioned above, cryptocurrency is not recognized as a financial instrument or shares in Slovenia, and thus transactions with it do not form a taxable base.
Taxation of cryptocurrencies in Slovenia for legal entities
For legal entities that own digital assets, tax issues are less obvious than for individuals. For example, those individuals who are registered as individual entrepreneurs and are engaged in the purchase and sale of cryptocurrency or mining, include all income from their activities in the taxable base. However, FURS prefers to treat legal entities individually. Their guidance states that “the financial accounting for such activities depends on the actual circumstances on a case-by-case basis”.
When assessing the tax burden of a legal entity, it is necessary to take into account the tax status of the recipient of income and the type of income. Thus, the mining of cryptocurrencies, the activities of the exchange, the acceptance of payments in bitcoins – all of this can have completely different tax consequences in Slovenia. For example, capital gains from cryptocurrencies completely fall into the tax base in Slovenia on the income of legal entities at a rate of 19%.
At the same time, it is important to note that Slovenian legislation prohibits basing the company’s business model solely on operations with cryptocurrency, that is, the activities of a payment operator with only one variant of transactions in bitcoins are also prohibited. All companies must have a bank account to carry out non-cash transactions with fiat funds.
VAT in Slovenia on Bitcoin transactions
Cryptocurrency mining in Slovenia is not a taxable VAT operation, therefore, VAT refunds on the purchase of mining equipment are also not allowed.
ICO taxation in Slovenia
In Slovenia, tokens used during ICOs do not differ from ordinary goods and services in terms of taxation, that is, the taxable base for tokens is determined by deducting the costs incurred for the acquisition or creation of a token from the proceeds received during its sale.


0 Comments