1. Geography and population of Latvia
Latvia is a bow tie country located in Eastern Europe. It borders four countries including Estonia to the north, Belarus to the southeast, Lithuania to the south, and Russia to the east. In addition, it is located along the coast of the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Riga. Riga is the capital and largest city located at the confluence of the Daugava River and the Gulf of Riga. The country covers an area of 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq. miles), almost the same as its neighbor, Lithuania.
General information about Latvia:
• Capital: Riga
• Area: 64,589 km²
• Telephone code: +371
• Top level domain: .lv
• Population: 1.86
Latvia consists of three main regions. Kurzeme is a hilly region in the west of the country. Vidzeme is the central region where the highest peak Gaiziņkalns is located. Latgale is another hill covered with forests and of great historical importance. Zemgale Plains is another notable region of Latvia, mostly with pronounced valleys.
The terrain in Latvia is flat and mostly low-lying plains. Although the area is flat and fertile, it also has a very pronounced maritime climate. In the east of Latvia, the terrain is more rugged and hilly. The highest point is Geising, which is 312 meters above sea level. While the lowest point is in the Baltic Sea.
Population of Latvia
The population of Latvia is 1.86 million people. Today, the country is struggling with a demographic catastrophe, just like its neighbors. The Baltic region as a whole has lost over 20% of its population since 1992. It is believed that this is the fastest depopulation region in the world. Latvia had no population growth since 1992.
Major cities of Latvia:
• Riga (capital): 742,572
• Daugavpils: 111,564
• Liepaja: 85,132
• Jelgava: 61,791
• Jurmala: 54,088
The birth rate in Latvia is currently around 1.34 children born per woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1. Young talented Latvians are leaving due to high unemployment and a lack of well-paid jobs.

2. Official language of Latvia
Latvian is the official and also the dominant language of Latvia. At the end of the 20th century, about 1.5 million Latvian speakers spoke Latvian. Today, native speakers make up 60% of the total population of the country. The Latvian government encourages the Latvian language in the country by including it in the country’s profile.
Latvia also speaks Russian, Ukrainian, Latgalian, and Belarusian. There are four other minority languages spoken in Latvia by about 0.6–1% of Latvian residents: Polish, Ukrainian, Belarusian, and Lithuanian. However, their use is mostly limited at the family level.
3. Currency in Latvia
Today in Latvia the Euro (EU) is used. Until December 2013, the national currency lats was used in the country. The ISO code is LVL, the common abbreviation is Ls. Interestingly, even if lats can no longer be used as a means of payment in Latvia, banknotes, and coins can still be exchanged for euros. To do this, citizens of Latvia use the Latvian National Bank or the ECB.
The transition from lats to the euro initially took place at a variable interest rate, which sometimes gave the lats the equivalent of up to two euros. When Latvia’s accession to the European Monetary Union became inevitable, the exchange rate was set above EUR 1.42288 per lat.
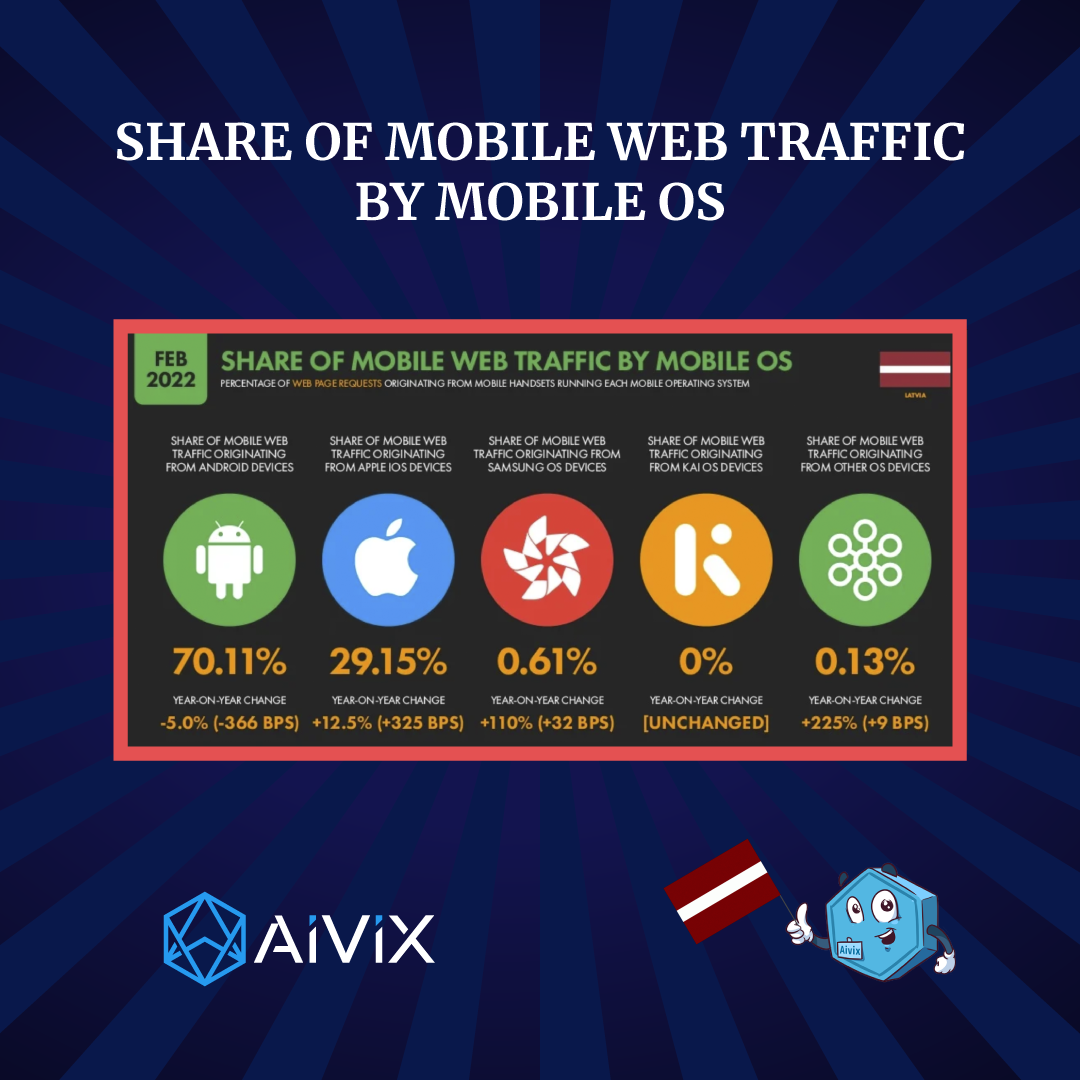
4. Internet in Latvia
In January 2022, there were 1.71 million internet users in Latvia. The internet use rate was 92% of the total population. Kepios analysis shows that the number of internet users in Latvia increased by 20,000 (+1.2%) between 2021 and 2022.
For perspective, this user data shows that 148.6 thousand people in Latvia were not using the Internet at the beginning of 2022, meaning that 8.0% of the population was not using the Internet in that period.
Internet connection speed in Latvia in 2022
Data published by Ookla shows that internet users in Latvia could expect the following internet connection speeds in early 2022:
• Average mobile Internet speed over cellular networks: 29.92 Mbps.
• Average fixed internet connection speed: 62.44 Mbps.
Ookla data shows that the average mobile internet speed in Latvia increased by 6.42 Mbps (+27.3%) in the twelve months to the start of 2022. During the same period, fixed internet connection speed in Latvia increased by 17.44 Mbps (+38.8%).
5. Economic development of Latvia
Since gaining independence from the USSR, Latvia has carried out significant market reforms. The country’s economy performed well thanks to the steady growth of domestic consumption and the contribution of foreign investment. As a member of the EU since 2004 (and the Eurozone since 2014), it has received significant European funding. Growth rates have been positive since 2011 and among the highest in the EU.
GDP per capita – 17 619 USD
After the economic downturn caused by the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, the country’s GDP rebounded sharply in 2021 (+4.5%) thanks to massive government support measures and robust export performance, combined with higher levels of private consumption. The latter should be the main growth driver over the forecast horizon, supported by strong wage growth and additional savings accumulated in recent years.
The driving force behind the Latvian economy is the service sector, which provides 64% of GDP and employs 69% of the active population. Thanks to attractive fiscal regulation, Latvia has a large financial services sector. Transport and ICT are also important activities for the country’s economy. Transport, in particular, provides 7.3% of GDP and employs over 8% of the workforce.
The banking sector includes 16 banks, including 13 credit institutions registered in Latvia, and three branches of European institutions (European Banking Federation).
Almost 30% of the territory of Latvia is intended for agricultural use, but since the beginning of the 90s of the last century, the structure of land management has changed significantly: collective farms were liquidated in favor of individual subsidiary farms, which currently dominate the country’s rural sector. Today, the share of the agricultural sector in GDP is 3.8%, and it employs 7.3% of the active population. It is dominated by livestock and dairy farming, as well as the production of cereals, sugar beets, potatoes, and vegetables.
The share of the industrial sector in GDP is 19.2%, it employs almost a quarter of the active labor force (23.7%). Industries such as construction, metallurgy, industrial food processing, and engineering are flourishing. Latvia is an important producer of railway equipment, radios, refrigerators, medicines, timber, and steel by-products.

6. Job in Latvia
The average salary in Latvia is 3,634 USD per year. The most typical earnings are $1,416 per month. The wages of men and women differ. Men earn an average of 9% more than women.
Average salaries by profession:
• Nurse: $1200
• Teacher: $950
• Waiter: $910
• Electrical engineer: $2000
• Dentist: $2200
• Administrator: $800
• Policeman: $600
• Programmer: $3000
The highest-paid occupations are management and business with an average income of $5,480 and a civil architect with an income of $5,300 per month. Based on the level of education, the highest salaries are received by people with a Ph.D. degree with a salary of $5,700 per month. The second-highest level of education is a master’s degree with a salary of $5,400 per month. Different experience also affects earnings. People with 16-20 years of work experience receive a salary of $5,600 per month. Employees with more than 20 years of experience receive from $6,000 per month.
7. Working days and holidays in Latvia
• January, 1st – New Year
• April, 15 – Good Friday
• April, 18 – Easter Monday
• May, 1st – Labor Day
• May, 4 – Independence Day
• June, 23 – Ligo (Midsummer Eve)
• June, 24 – Jani (Saint John’s Day)
• November, 18 – Proclamation of the Republic
• December, 24 – Christmas Eve
• December, 25 – Christmas
• December, 26 – Second Day of Christmas
• December, 31 – New Year’s Eve

8. Latvian mentality
The mentality of Latvians is usually very similar to the Scandinavians: they are reserved and do not openly express their emotions. As a rule, Latvians do not like small talk. People in Latvia do not speak loudly in public. Shouting or whistling in public is considered rude. This applies to restaurants, cafes, public transport, and other public places.
In Latvia, a low-context culture of communication has been adopted, when communication does not require a large amount of background information. Excessive explanation of anything can be perceived as disrespectful. When asking questions, it’s best to be specific and direct.
The identity of Latvians is linked to their family’s home region. Latvians rarely decide to leave the area where they were born. Even if young people leave in search of work or education, they return to their hometowns for holidays and summers.
9. Advertising in Latvia
Consumers in Latvia respond best to advertisements in print or electronic media. The leading daily newspapers in Latvian are:
• Diana;
• Latvian Avize;
• Neatkariga Rita Avize;
• Dienas Business.
Many Latvians, especially young people, get most of their information online through Twitter, Draugiem.lv (the Latvian version of Facebook), and Facebook, as well as popular online portals such as Delfi.lv and TVNet.lv. There are also many local and niche newspapers and magazines in each city.
In terms of important characteristics of the offer, the price is the most important factor in consumer spending in Latvia, ahead of the quality of the goods and the characteristics of the seller. Consumers spend a significant portion of their income on food, as well as housing and communal services, yet their share of total spending has been declining in recent years. Wealthier consumers are brand aware and willing to pay a higher price for their favorite brand.

10. Cryptocurrency in Latvia
The position of the Bank of Latvia and the State Revenue Service is that cryptocurrency is a contractual and not a legal means of payment that can be used in exchange transactions. And while Latvia is aiming to become a leader in fintech, its work to regulate cryptocurrencies has only just begun, following in the footsteps of neighboring Lithuania.
Today, citizens of Latvia can convert, buy and sell cryptocurrencies for fiat. It is estimated that more than 62 thousand people, 3.3% of the total population of Latvia, currently own at least one form of cryptocurrency.
According to the 2020 Small Business Economics Survey, Latvia ranks among the top 15 countries in the world in terms of total bitcoin merchants per million users, as well as bitnode usage intensity, indicating high commercial adoption of bitcoin in Latvia.



0 Comments